Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nakamura, Hideo; Bentaib, A.*; Herranz, L. E.*; Ruyer, P.*; Mascari, F.*; Jacquemain, D.*; Adorni, M.*
Proceedings of International Conference on Topical Issues in Nuclear Installation Safety; Strengthening Safety of Evolutionary and Innovative Reactor Designs (TIC 2022) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2022/10
Mascari, F.*; Bersano, A.*; Woods, B. G.*; Reyes, J. N.*; Welter, K.*; Nakamura, Hideo; D'Auria, F.*
Proceedings of 19th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-19) (Internet), 16 Pages, 2022/03
 sp
sp Hard Rock Laboratory in Sweden
Hard Rock Laboratory in SwedenTachi, Yukio; Ito, Tsuyoshi*; Gylling, B.*
Water Resources Research, 57(11), p.e2020WR029335_1 - e2020WR029335_20, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:18.22(Environmental Sciences)This paper focuses on the scaling approach for sorption and diffusion parameters from laboratory to in-situ conditions using the dataset of LTDE-SD experiment performed at the  sp
sp HRL. The near-surface heterogeneities at both fracture surface and rock matrix could be evaluated by conceptual model with high porosity and diffusivity, and sorption capacity, and their gradual change at the near-surface zones. The modelling results for non-sorbing Cl-36 and weak-sorbing Na-22 could validate the model concept and the parameter estimation of porosity and diffusivity, by considering the disturbed zone of 5 mm thickness with gradual parameter changes. The De values of these cationic and anionic tracers showed typical cation excess and anion exclusion effects. The modelling results for high sorbing tracers (Cs-137, Ra-226, Ni-63 and Np-237) with different sorption mechanism could confirm the validity of the scaling approaches of Kd values as a function of particle size and their relation to the near-surface disturbances.
HRL. The near-surface heterogeneities at both fracture surface and rock matrix could be evaluated by conceptual model with high porosity and diffusivity, and sorption capacity, and their gradual change at the near-surface zones. The modelling results for non-sorbing Cl-36 and weak-sorbing Na-22 could validate the model concept and the parameter estimation of porosity and diffusivity, by considering the disturbed zone of 5 mm thickness with gradual parameter changes. The De values of these cationic and anionic tracers showed typical cation excess and anion exclusion effects. The modelling results for high sorbing tracers (Cs-137, Ra-226, Ni-63 and Np-237) with different sorption mechanism could confirm the validity of the scaling approaches of Kd values as a function of particle size and their relation to the near-surface disturbances.
Idomura, Yasuhiro
Physics of Plasmas, 26(12), p.120703_1 - 120703_5, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:33.86(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)This Letter presents the impacts of the hydrogen isotope mass and the normalized gyroradius 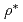 on L-mode like hydrogen (H) and deuterium (D) plasmas dominated by ion temperature gradient driven (ITG) turbulence using global full-f gyrokinetic simulations. In ion heated numerical experiments with adiabatic electrons, the energy confinement time shows almost no isotope mass dependency, and is determined by Bohm like
on L-mode like hydrogen (H) and deuterium (D) plasmas dominated by ion temperature gradient driven (ITG) turbulence using global full-f gyrokinetic simulations. In ion heated numerical experiments with adiabatic electrons, the energy confinement time shows almost no isotope mass dependency, and is determined by Bohm like 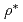 scaling. Electron heated numerical experiments with kinetic electrons show clear isotope mass dependency caused by the isotope effect on the collisional energy transfer from electrons to ions, and the H and D plasmas show similar ion and electron temperature profiles at an H to D heating power ratio of
scaling. Electron heated numerical experiments with kinetic electrons show clear isotope mass dependency caused by the isotope effect on the collisional energy transfer from electrons to ions, and the H and D plasmas show similar ion and electron temperature profiles at an H to D heating power ratio of 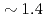 . The normalized collisionless ion gyrokinetic equations for H and D plasmas become identical at the same
. The normalized collisionless ion gyrokinetic equations for H and D plasmas become identical at the same 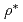 , and collisions weakly affect ITG turbulence. Therefore, the isotope mass dependency is mainly contributed by the
, and collisions weakly affect ITG turbulence. Therefore, the isotope mass dependency is mainly contributed by the 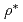 scaling and the heating sources.
scaling and the heating sources.
Sugino, Kazuteru; Numata, Kazuyuki*; Ishikawa, Makoto; Takeda, Toshikazu*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 130, p.118 - 123, 2019/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)In MA sample irradiation test data calculations, the neutron fluence during irradiation period is generally scaled by using dosimetry data in order to improve calculation accuracy. In such a case, appropriate correction is required to burnup sensitivity coefficients obtained by the conventional generalized perturbation theory because some cancellations occur in the burnup sensitivity coefficients. Therefore, a new formula for the burnup sensitivity coefficient has been derived with the consideration of the neutron fluence scaling effect (NFS). In addition, the cross-section-induced uncertainty is evaluated by using the obtained burnup sensitivity coefficients and the covariance data based on the JENDL-4.0.
Nakamura, Hideo
Proceedings of ANS International Conference on Best Estimate Plus Uncertainties Methods (BEPU 2018) (USB Flash Drive), 8 Pages, 2018/00
no abstracts in English
Nakamura, Hideo
Proceedings of Seminar on the Transfer of Competence, Knowledge and Experience gained through CSNI Activities in the Field of Thermal-Hydraulics (THICKET 2016) (CD-ROM), 29 Pages, 2016/06
no abstracts in English
Mascari, F.*; Nakamura, Hideo; Umminger, K.*; De Rosa, F.*; D'Auria, F.*
Proceedings of 16th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-16) (USB Flash Drive), p.4921 - 4934, 2015/08
Takizuka, Tomonori; Urano, Hajime; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Oyama, Naoyuki
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 48(6), p.799 - 806, 2006/06
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:48.35(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Dependence of the ELMy H-mode confinement on the beta has been investigated for a long time, but a common conclusion has not yet been obtained.The IPB98(y,2) scaling shows a strong degradation with beta, while DIII-D and JET experiments exhibited the absence of the beta degradation. Recent JT-60U experiment demonstrated that the strong beta degradation really exists for the ELMy H-mode. In the present paper, we analyze the JT-60U ELMy H-mode confinement database and confirm the strong power degradation of the confinement time, which corresponds to the strong beta degradation consistent with the above result. We analyze also the ITPA H-mode confinement database in detail. How the beta dependence of the confinement time is changed by the externally given parameters, such as the shape parameters, are investigated.
Kusakabe, Toshio*; Shiota, Kenji*; Kubo, Hirotaka; Shirai, Toshizo*
Journal of Plasma and Fusion Research SERIES, Vol.7, p.237 - 239, 2006/00
no abstracts in English
 and collisionality approaching ITER conditions
and collisionality approaching ITER conditionsCordey, J. G.*; Thomsen, K.*; Chudnovskiy, A.*; Kardaun, O. J. W. F.*; Takizuka, Tomonori; Snipes, J. A.*; Greenwald, M.*; Sugiyama, L.*; Ryter, F.*; Kus, A.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 45(9), p.1078 - 1084, 2005/09
Times Cited Count:51 Percentile:82.4(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The condition of the latest version of the ELMy H-mode database has been re-examined. It is shown that there is bias in the ordinary least squares regression for some of the variables. To address these shortcomings three different techniques are employed: (a)principal component regression, (b)an error in variables technique and (c)the selection of a better conditioned dataset with fewer variables. Scalings in terms of the dimensionless physics valiables, as well as the standard set of engineering variables, are derived. The new scalings give a very similar performance for existing scalings for ITER at the standard beta, but a much improvement performance at higher beta.
Takeda, Nobukazu; Nakahira, Masataka
JAERI-Tech 2004-073, 59 Pages, 2005/01
The ITER toamak is composed of major components such as superconducting magnet and vacuum vessel whose operation temperatures are changed from room temperature to 4 K and room temperature to 200 C, respectively. The gravity support of the tokamak is flexible in order to accept the thermal deformation caused by temperature change. This structural feature causes the complex behaviors of the tokamak during seismic events. Therefore, the mechanical characteristics of the flexible support have to be investigated in detail. The present report describes the global plan of the series of vibration tests to estimate the seismic performance of the ITER tokamak. Although it is ideal that the vibration tests are carried out using a full-scale model, scale models are planned due to the limitation of the test facilities. The test results can be estimated by a scaling law. When the scaling law cannot be applied to some performances, the test is performed using a full-scale model. In addition, the other tests such as vacuum vessel and small-scaled models of the support structure are also planned.
C, respectively. The gravity support of the tokamak is flexible in order to accept the thermal deformation caused by temperature change. This structural feature causes the complex behaviors of the tokamak during seismic events. Therefore, the mechanical characteristics of the flexible support have to be investigated in detail. The present report describes the global plan of the series of vibration tests to estimate the seismic performance of the ITER tokamak. Although it is ideal that the vibration tests are carried out using a full-scale model, scale models are planned due to the limitation of the test facilities. The test results can be estimated by a scaling law. When the scaling law cannot be applied to some performances, the test is performed using a full-scale model. In addition, the other tests such as vacuum vessel and small-scaled models of the support structure are also planned.
Chikazumi, Shimpei*; Iwamoto, Akira
Chaos, Solitons and Fractals, 23(1), p.73 - 78, 2005/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Mathematics, Interdisciplinary Applications)To seek for a possible origin of fractal pattern in nature, we perform a molecular dynamics simulation for a fragmentation of an infinite fcc lattice. The fragmentation is induced by the initial condition of the model that the lattice particles have the Hubble-type radial expansion velocities. As time proceeds, the average density decreases and density fluctuation develops. By using the box counting method, it is found that the frequency-size plot of the density follows instantaneously a universal power-law for each Hubble constant up to the size of a cross-over. This cross-over size corresponds to the maximum size of fluctuation and is found to obey a dynamical scaling law as a function of time. This instantaneous generation of a nascent fractal is purely of dynamical origin and it shows us a new formation mechanism of a fractal patters different from the traditional criticality concept.
Matsubayashi, Masahito; Hibiki, Takashi*; Mishima, Kaichiro*; Yoshii, Koji*; Okamoto, Koji*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 533(3), p.481 - 490, 2004/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:30.89(Instruments & Instrumentation)The validity of a fast neutron radiography quantification method, the  -scaling method, which was originally proposed for thermal neutron radiography was examined with Monte Carlo calculations and experiments conducted at the YAYOI fast neutron source reactor. Water and copper were selected as comparative samples for a thermal neutron radiography case and a dense object, respectively. Although different characteristics on effective macroscopic cross-sections were implied by the simulation, the
-scaling method, which was originally proposed for thermal neutron radiography was examined with Monte Carlo calculations and experiments conducted at the YAYOI fast neutron source reactor. Water and copper were selected as comparative samples for a thermal neutron radiography case and a dense object, respectively. Although different characteristics on effective macroscopic cross-sections were implied by the simulation, the  -scaled experimental results with the fission neutron spectrum cross-sections were well fitted to the measurements for both the water and copper samples. This indicates that the
-scaled experimental results with the fission neutron spectrum cross-sections were well fitted to the measurements for both the water and copper samples. This indicates that the  -scaling method could be successfully adopted for quantitative measurements in fast neutron radiography.
-scaling method could be successfully adopted for quantitative measurements in fast neutron radiography.
Yamamoto, Kazuyoshi; Kumada, Hiroaki; Kishi, Toshiaki; Torii, Yoshiya; Sakurai, Yoshinori*; Kobayashi, Toru*
Proceedings of 11th World Congress on Neutron Capture Therapy (ISNCT-11) (CD-ROM), 15 Pages, 2004/10
To carry out the boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) using the epithermal neutron, the epithermal neutron beam intensity was measured by using  Au reaction rate activated on the resonance absorption peak (4.9eV). Two scaling factors, which are the reactor power calibration factor and the calculation/experiment (C/E) scaling factor, are necessary in order to correct with the simulation and actual irradiation experiment. First, an optimum detector position was investigated using MCNP code. The result of MCNP calculation showed that the influence of subject placed at the collimator was below 1% when the detector was placed in the distance of over 20cm from the collimator. Therefore we installed the monitor holders near the bismuth block in order to set three gold wire monitors. The factors were determined in the calibration experiments that measure the thermal neutron flux in the phantom and reaction rate of the gold wire monitors. The monitoring technique to measure epithermal neutron beam intensity was applied to clinical irradiation with the epithermal neutron beam.
Au reaction rate activated on the resonance absorption peak (4.9eV). Two scaling factors, which are the reactor power calibration factor and the calculation/experiment (C/E) scaling factor, are necessary in order to correct with the simulation and actual irradiation experiment. First, an optimum detector position was investigated using MCNP code. The result of MCNP calculation showed that the influence of subject placed at the collimator was below 1% when the detector was placed in the distance of over 20cm from the collimator. Therefore we installed the monitor holders near the bismuth block in order to set three gold wire monitors. The factors were determined in the calibration experiments that measure the thermal neutron flux in the phantom and reaction rate of the gold wire monitors. The monitoring technique to measure epithermal neutron beam intensity was applied to clinical irradiation with the epithermal neutron beam.
Nishimori, Nobuyuki
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 528(1-2), p.34 - 38, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.3(Instruments & Instrumentation)The sustained saturation in an FEL oscillator at zero detuning of an optical cavity (
 =0) is studied analytically. The FEL field at
=0) is studied analytically. The FEL field at 
 =0 is characteristic of self-amplified spontaneous emission (SASE) FEL. For both cases, the field is composed of the forward incoherent and subsequent coherent states. The coherent field at
=0 is characteristic of self-amplified spontaneous emission (SASE) FEL. For both cases, the field is composed of the forward incoherent and subsequent coherent states. The coherent field at 
 =0 evolves with round trips due to the lethargy. The field at saturation is similar to that of the leading edge of SASE FEL with high electron beam density. It is found that the peak intensity and the pulse length of the saturation field scale with fundamental FEL parameter and an optical cavity loss.
=0 evolves with round trips due to the lethargy. The field at saturation is similar to that of the leading edge of SASE FEL with high electron beam density. It is found that the peak intensity and the pulse length of the saturation field scale with fundamental FEL parameter and an optical cavity loss.
Kusakabe, Toshio*; Miyamoto, Yoshiharu*; Ishida, Rikiya*; Ito, Kojiro*; Kuroyanagi, Nobuhiro*; Nakai, Yota*; Shirai, Toshizo
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 205, p.600 - 604, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:43.07(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Neyatani, Yuzuru; Nakamura, Yukiharu; Yoshino, Ryuji; Hatae, Takaki; JT-60 Team
Fusion Energy 1998, p.859 - 862, 1998/10
no abstracts in English
Kaye, S. M.*; Greenwald, M. J.*; U.Stroth*; O.Kardaun*; A.Kus*; Schissel, D. R.*; J.DeBoo*; Bracco, G.*; K.Thomsen*; Cordey, J. G.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 37(9), p.1303 - 1328, 1997/00
Times Cited Count:162 Percentile:96.76(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
 ,CH
,CH ,C
,C H
H ,C
,C H
H and CO
and CO molecules
moleculesIto, Akio*; Imanishi, Nobutsugu*; *; Hamamoto, Nariaki*; *; Tanaka, Takashi*; *; Saito, Manabu*; Haruyama, Yoichi*; Shirai, Toshizo
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 64(9), p.3255 - 3264, 1995/09
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:70.71(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English